

|
DNV to host webinar on FuelEU Maritime compliance strategies
Classification society offers insights as first reporting period closes and verification phase begins. |
|
|
|
||

|
Biodiesel–MGO price spread narrows to $400–500/mt in Northwest Europe
Bunker One says tighter spread creates opportunities for shipping companies pursuing decarbonisation targets. |
|
|
|
||

|
Exmar to discuss ammonia-fuelled vessel operations in webinar
Shipowner will explore safety measures and partnerships for new dual-fuel ammonia carriers. |
|
|
|
||

|
Skuld reports engine damage from CNSL biofuel blends amid rising alternative fuel adoption
Marine insurer details operational challenges with biofuels, including FAME, CNSL and UCOME across member vessels. |
|
|
|
||

|
GRM and Bunker Holding to host webinar on Middle East war's impact on energy markets
Webinar on 9 March will examine effects on crude oil, bunker and gas markets. |
|
|
|
||
|
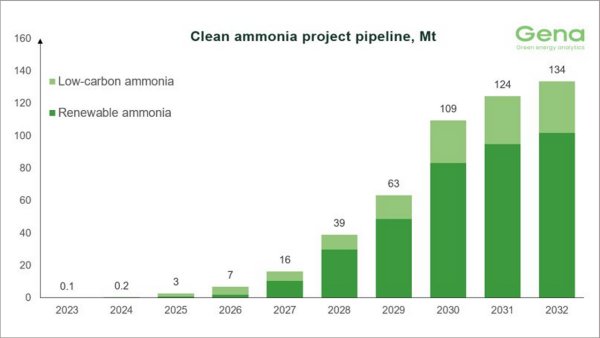
Clean ammonia project pipeline reaches 145 MMT by 2034, but delivery concerns mount
GENA Solutions reports 325 tracked projects, though over 70 have been frozen in 20 months. |
|
|
|
||

|
Peninsula highlights supply chain strength amid Strait of Hormuz closure
Marine fuel seller emphasises reliability as geopolitical disruption reshapes global bunker markets. |
|
|
|
||

|
World Shipping Council backs EU maritime strategies but calls for faster trade simplification
Industry body supports port security and decarbonisation measures while urging action on customs barriers. |
|
|
|
||

|
Anemoi and Lloyd’s Register call for unified approach to wind propulsion performance verification
Anemoi Marine Technologies and Lloyd’s Register publish paper advocating alignment of verification methodologies. |
|
|
|
||

|
Smyril Line's methanol-ready ro-ro launched in China
First of two 3,300 lane-metre vessels floated out for Faroese operator. |
|
|
|
||
| California At-Berth Regulation advisory becomes effective in January 2017 [News & Insights] |
| Los Angeles holds the line on emissions targets [News & Insights] |
| Shipping firms fined $1.3m for dumping oily waste and cover-up [News & Insights] |
| LA and Long Beach propose 'bold strategies' to slash emissions [News & Insights] |