

|
TFG Marine calls for digital transformation to manage alternative fuel risks
CFO says transparency and digital solutions are essential as the marine fuels sector faces volatility from diversification. |
|
|
|
||

|
Reganosa’s Mugardos terminal adds bio-LNG bunkering for ships and trucks
Spanish facility obtains EU sustainability certification to supply renewable fuel with 92% lower emissions. |
|
|
|
||

|
Growth Energy joins Global Ethanol Association as new member
US biofuel trade association represents nearly 100 biorefineries and over half of US ethanol production. |
|
|
|
||

|
H2SITE explains decision to establish Bergen subsidiary
Spanish firm says Norwegian city was obvious choice for its ambitions. |
|
|
|
||

|
Christiania Energy relocates headquarters within Odense Harbour
Bunker firm moves to larger waterfront office to accommodate growing team and collaboration needs. |
|
|
|
||

|
HD Hyundai Heavy Industries receives design approval for 20,000-cbm LNG bunkering vessel
Bureau Veritas grants approval in principle following joint development project with South Korean shipbuilder. |
|
|
|
||

|
Peninsula outlines dual role in FuelEU Maritime compliance at Lloyd’s Register panel
Marine fuel supplier discusses challenges for shipowners and opportunities for suppliers under new regulation. |
|
|
|
||
|
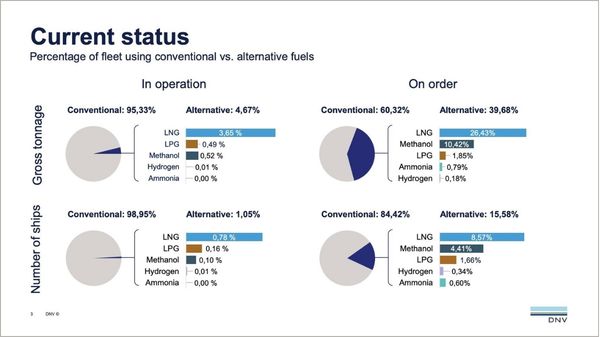
LNG-fuelled container ships dominate January alternative-fuel vessel orders
Container ships accounted for 16 of 20 alternative-fuelled vessels ordered in January, DNV reports. |
|
|
|
||

|
GCMD and CIMAC sign partnership to advance alternative marine fuel readiness
Two-year agreement aims to bridge operational experience with technical standards for decarbonisation solutions. |
|
|
|
||
|
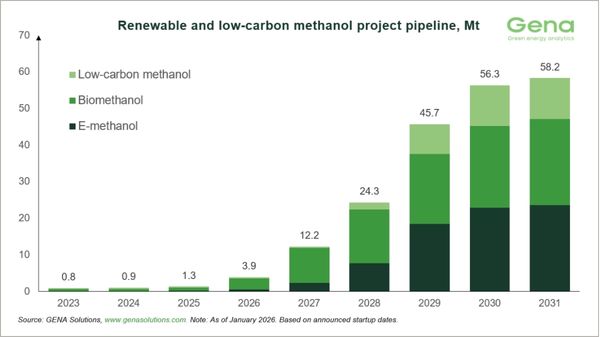
Renewable methanol project pipeline reaches 58.2m tonnes by 2031, GENA reports
Project Navigator Methanol tracks 275 projects, including e-methanol, biomethanol and low-carbon methanol facilities globally. |
|
|
|
||
| Interlake Steamship to install more scrubbers [News & Insights] |