
|
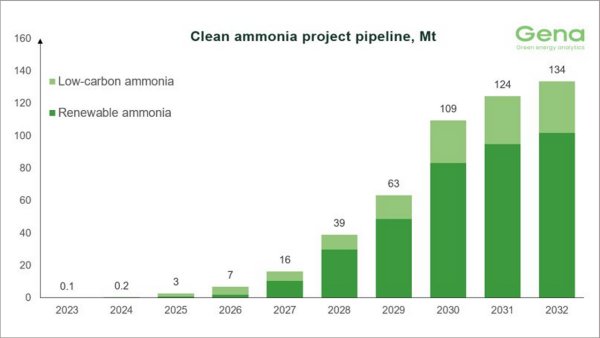
Clean ammonia project pipeline reaches 145 MMT by 2034, but delivery concerns mount
GENA Solutions reports 325 tracked projects, though over 70 have been frozen in 20 months. |
|
|
|
||

|
Peninsula highlights supply chain strength amid Strait of Hormuz closure
Marine fuel seller emphasises reliability as geopolitical disruption reshapes global bunker markets. |
|
|
|
||

|
World Shipping Council backs EU maritime strategies but calls for faster trade simplification
Industry body supports port security and decarbonisation measures while urging action on customs barriers. |
|
|
|
||

|
Anemoi and Lloyd’s Register call for unified approach to wind propulsion performance verification
Anemoi Marine Technologies and Lloyd’s Register publish paper advocating alignment of verification methodologies. |
|
|
|
||

|
Smyril Line's methanol-ready ro-ro launched in China
First of two 3,300 lane-metre vessels floated out for Faroese operator. |
|
|
|
||
|
ICS webinar explores regulatory framework for nuclear-powered merchant ships
Industry experts discuss the timeline and challenges for adopting nuclear propulsion in the commercial shipping sector. |
|
|
|
||

|
Oilmar DMCC seeks senior bunker trader for Dubai office
Dubai-based energy trader recruiting for Middle East, Indian subcontinent and Africa trade flows. |
|
|
|
||

|
Oilmar DMCC seeks bunker traders for Singapore office
Dubai-based trader recruiting mid-level and senior professionals to expand Asia-Pacific marine fuels operations. |
|
|
|
||

|
ClassNK updates EU shipping emissions guidance for LNG-fuelled vessels
Japanese classification society releases revised FAQs addressing methane slip measurement procedures. |
|
|
|
||

|
Bureau Veritas delivers first 15,000-teu methanol dual-fuel container ship for CMA CGM
Classification society completes delivery of CMA CGM Monte Cristo built by DSIC Tianjin. |
|
|
|
||
| Italian firm orders Hamworthy scrubbers [News & Insights] |
| Krystallon scrubber on EPA Emerging Technology List [News & Insights] |
| Wärtsilä in scrubber system partnership [News & Insights] |
| Agreement to develop dry scrubbing technology [News & Insights] |